音乐频谱显示 FFT of waveIn audio signals. Free source code and programming help_基于mattab音乐文件的频谱动态显示代码-程序员宅基地
技术标签: components im fft 语音技术 c++&vc audio signal 音乐



![]()

Introduction
The Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) allows users to view the spectrum content of an audio signal. The FFT code presented here was written by Don Cross, his homepage appears to have subsequently been taken down. Rather than explain the mathematical theory of the FFT, I will attempt to explain its usefulness as it relates to audio signals.
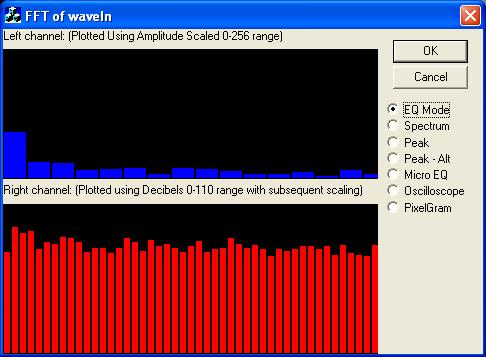
The FFT allows users to obtain the spectral makeup of an audio signal, obtain the decibels of its various frequencies, or obtain the intensity of its various frequencies. Spectral viewers (shown in the image above), Equalizers, or VU-Meters may all use the FFT in order to display their results. The difference between them then depends upon one of a couple of equations that take the real and imaginary components of the FFT, and return either the intensity or decibel levels to be used in the graphed result. The following code takes both the real and imaginary components of the FFT result, and returns the intensity and decibels.
inline double GetFrequencyIntensity(double re, double im) { return sqrt((re*re)+(im*im)); } #define mag_sqrd(re,im) (re*re+im*im) #define Decibels(re,im) ((re == 0 && im == 0) ? (0) : 10.0 * log10(double(mag_sqrd(re,im)))) #define Amplitude(re,im,len) (GetFrequencyIntensity(re,im)/(len)) #define AmplitudeScaled(re,im,len,scale) ((int)Amplitude(re,im,len)%scale)
The FFT uses the audio signal as its real component, and uses a NULL pointer for its imaginary component indicating that the imaginary data does not exist. Upon its return, the FFT will return both the real and imaginary data components based upon the data given as the real component. The is mirrored with the return samples so that 0-FFT_LEN/2 contains the data, and FFT_LEN/2 to FFT_LEN contains a reverse of the data. This mistake was corrected in my code. The code that performs the FFT follows:
DWORD nCount = 0; for (DWORD dw = 0; dw < FFT_LEN; dw++) { { //copy audio signal to fft real component for left channel finleft[nCount] = (double)((short*)pwh->lpData)[dw++]; //copy audio signal to fft real component for right channel finright[nCount++] = (double)((short*)pwh->lpData)[dw]; } } //Perform FFT on left channel fft_double(FFT_LEN/2,0,finleft,NULL,fout,foutimg); float re,im,fmax=-99999.9f,fmin=99999.9f; for(int i=1;i < FFT_LEN/4-1;i++) //Use FFT_LEN/4 since the data is mirrored within the array. { re = fout[i]; im = foutimg[i]; //get amplitude and scale to 0..256 range fdraw[i]=AmplitudeScaled(re,im,FFT_LEN/2,256); if (fdraw[i] > fmax) { fmax = fdraw[i]; } if (fdraw[i] < fmin) { fmin = fdraw[i]; } } //Use this to send the average band amplitude to something int nAvg, nBars=16, nCur = 0; for(int i=1;i < FFT_LEN/4;i++) { nAvg = 0; for (int n=0; n < nBars; n++) { nAvg += (int)fdraw[i]; } nAvg /= nBars; //Send data here to something, //nothing to send it to so we print it. TRACE("Average for Bar#%d is %d/n",nCur++,nAvg); i+=nBars-1; } DataHolder* pDataHolder = (DataHolder*)lpData; // Draw left channel CFrequencyGraph* pPeak = (CFrequencyGraph*)pDataHolder->pData; if (::IsWindow(pPeak->GetSafeHwnd())) { pPeak->SetYRange(0,256); pPeak->Update(FFT_LEN/4,fdraw); } // Perform FFT on right channel fmax=-99999.9f,fmin=99999.9f; fft_double(FFT_LEN/2,0,finright,NULL,fout,foutimg); fdraw[0] = fdraw[FFT_LEN/4] = 0; for(i=1;i < FFT_LEN/4-1;i++) //Use FFT_LEN/4 since the data is mirrored within the array. { re = fout[i]; im = foutimg[i]; //get Decibels in 0-110 range fdraw[i] = Decibels(re,im); if (fdraw[i] > fmax) { fmax = fdraw[i]; } if (fdraw[i] < fmin) { fmin = fdraw[i]; } } //Draw right channel CFrequencyGraph* pPeak2 = (CFrequencyGraph*)pDataHolder->pData2; if (::IsWindow(pPeak2->GetSafeHwnd())) { pPeak2->SetNumberOfSteps(50); //Use updated dynamic range for scaling pPeak2->SetYRange((int)fmin,(int)fmax); pPeak2->Update(FFT_LEN/4,fdraw); }
This code is contained in a callback function that is called every time the waveIn functions return with updated audio signal data. The code that actually performs the FFT looks like:
void fft_double (unsigned int p_nSamples, bool p_bInverseTransform, double *p_lpRealIn, double *p_lpImagIn, double *p_lpRealOut, double *p_lpImagOut) { if(!p_lpRealIn || !p_lpRealOut || !p_lpImagOut) return; unsigned int NumBits; unsigned int i, j, k, n; unsigned int BlockSize, BlockEnd; double angle_numerator = 2.0 * PI; double tr, ti; if( !IsPowerOfTwo(p_nSamples) ) { return; } if( p_bInverseTransform ) angle_numerator = -angle_numerator; NumBits = NumberOfBitsNeeded ( p_nSamples ); for( i=0; i < p_nSamples; i++ ) { j = ReverseBits ( i, NumBits ); p_lpRealOut[j] = p_lpRealIn[i]; p_lpImagOut[j] = (p_lpImagIn == NULL) ? 0.0 : p_lpImagIn[i]; } BlockEnd = 1; for( BlockSize = 2; BlockSize <= p_nSamples; BlockSize <<= 1 ) { double delta_angle = angle_numerator / (double)BlockSize; double sm2 = sin ( -2 * delta_angle ); double sm1 = sin ( -delta_angle ); double cm2 = cos ( -2 * delta_angle ); double cm1 = cos ( -delta_angle ); double w = 2 * cm1; double ar[3], ai[3]; for( i=0; i < p_nSamples; i += BlockSize ) { ar[2] = cm2; ar[1] = cm1; ai[2] = sm2; ai[1] = sm1; for ( j=i, n=0; n < BlockEnd; j++, n++ ) { ar[0] = w*ar[1] - ar[2]; ar[2] = ar[1]; ar[1] = ar[0]; ai[0] = w*ai[1] - ai[2]; ai[2] = ai[1]; ai[1] = ai[0]; k = j + BlockEnd; tr = ar[0]*p_lpRealOut[k] - ai[0]*p_lpImagOut[k]; ti = ar[0]*p_lpImagOut[k] + ai[0]*p_lpRealOut[k]; p_lpRealOut[k] = p_lpRealOut[j] - tr; p_lpImagOut[k] = p_lpImagOut[j] - ti; p_lpRealOut[j] += tr; p_lpImagOut[j] += ti; } } BlockEnd = BlockSize; } if( p_bInverseTransform ) { double denom = (double)p_nSamples; for ( i=0; i < p_nSamples; i++ ) { p_lpRealOut[i] /= denom; p_lpImagOut[i] /= denom; } } }
And it requires the following supporting functions:
/// // check is a number is a power of 2 /// bool IsPowerOfTwo( unsigned int p_nX ) { if( p_nX < 2 ) return false; if( p_nX & (p_nX-1) ) return false; return true; } /// // return needed bits for fft /// unsigned int NumberOfBitsNeeded( unsigned int p_nSamples ) { int i; if( p_nSamples < 2 ) { return 0; } for ( i=0; ; i++ ) { if( p_nSamples & (1 << i) ) return i; } } /// // ? /// unsigned int ReverseBits(unsigned int p_nIndex, unsigned int p_nBits) { unsigned int i, rev; for(i=rev=0; i < p_nBits; i++) { rev = (rev << 1) | (p_nIndex & 1); p_nIndex >>= 1; } return rev; } /// // return a frequency from the basefreq and num of samples /// double Index_to_frequency(unsigned int p_nBaseFreq, unsigned int p_nSamples, unsigned int p_nIndex) { if(p_nIndex >= p_nSamples) { return 0.0; } else if(p_nIndex <= p_nSamples/2) { return ( (double)p_nIndex / (double)p_nSamples * p_nBaseFreq ); } else { return ( -(double)(p_nSamples-p_nIndex) / (double)p_nSamples * p_nBaseFreq ); } }
The included sample class, CFrequencyGraph, will draw a sample EQ, peak meter, and spectral graph using the frequency intensity. Hopefully, this serves as a decent introduction to the uses and basics of the Fast Fourier Transform for audio signals. Other functions of the FFT include using it in combination with a Beat Detection Algorithm to detect beats in an audio signal. Another page with useful FFT information is located at FFT Spectrum Analyser.
This article uses waveIn* functions to retrieve the soundcard's data from the playing source. Therefore, you must manually open your soundcard properties and change the recording source to use mono/stereo mix or waveIn as the selected recording line. Also, if you set the playback wave option to false, this will override the recording options and no sound will appear. For information about doing an inverse FFT for transforming frequencies into an audio signal, please do a Google search on "Inverse FFT" or "IFFT".
History
- Version 1.3: Fixed Spectrum drawing, Changed Pixelgram color, changed Process routine to match new Recording parameters.
- Version 1.2: Fixed many drawing bugs, changed to use amplitude scaled and decibels.
智能推荐
JavaScript学习笔记_curry函数未定义-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读343次。五种原始的变量类型1.Undefined--未定义类型 例:var v;2.String -- ' '或" "3.Boolean4.Number5.Null--空类型 例: var v=null;Number中:NaN -- not a number非数本身是一个数字,但是它和任何数字都不相等,代表非数,它和自己都不相等判断是不是NaN不能用=_curry函数未定义
兑换码编码方案实践_优惠券编码规则-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.2w次,点赞2次,收藏17次。兑换码编码设计当前各个业务系统,只要涉及到产品销售,就离不开大大小小的运营活动需求,其中最普遍的就是兑换码需求,无论是线下活动或者是线上活动,都能起到良好的宣传效果。兑换码:由一系列字符组成,每一个兑换码对应系统中的一组信息,可以是优惠信息(优惠券),也可以是相关奖品信息。在实际的运营活动中,要求兑换码是唯一的,每一个兑换码对应一个优惠信息,而且需求量往往比较大(实际上的需求只有预期_优惠券编码规则
c语言周林答案,C语言程序设计实训教程教学课件作者周林ch04结构化程序设计课件.ppt...-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读45次。C语言程序设计实训教程教学课件作者周林ch04结构化程序设计课件.ppt* * 4.1 选择结构程序设计 4.2 循环结构程序设计 4.3 辅助控制语句 第四章 结构化程序设计 4.1 选择结构程序设计 在现实生活中,需要进行判断和选择的情况是很多的: 如果你在家,我去拜访你 如果考试不及格,要补考 如果遇到红灯,要停车等待 第四章 结构化程序设计 在现实生活中,需要进行判断和选择的情况..._在现实生活中遇到过条件判断的问
幻数使用说明_ioctl-number.txt幻数说明-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读999次。幻数使用说明 在驱动程序中实现的ioctl函数体内,实际上是有一个switch{case}结构,每一个case对应一个命令码,做出一些相应的操作。怎么实现这些操作,这是每一个程序员自己的事情。 因为设备都是特定的,这里也没法说。关键在于怎样组织命令码,因为在ioctl中命令码是唯一联系用户程序命令和驱动程序支持的途径 。 命令码的组织是有一些讲究的,因为我们一定要做到命令和设备是一一对应的,利_ioctl-number.txt幻数说明
ORB-SLAM3 + VScode:检测到 #include 错误。请更新 includePath。已为此翻译单元禁用波浪曲线_orb-slam3 include <system.h> 报错-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读399次。键盘按下“Shift+Ctrl+p” 输入: C++Configurations,选择JSON界面做如下改动:1.首先把 “/usr/include”,放在最前2.查看C++路径,终端输入gcc -v -E -x c++ - /usr/include/c++/5 /usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/c++/5 /usr/include/c++/5/backward /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/5/include /usr/local/_orb-slam3 include 报错
「Sqlserver」数据分析师有理由爱Sqlserver之十-Sqlserver自动化篇-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读129次。本系列的最后一篇,因未有精力写更多的入门教程,上篇已经抛出书单,有兴趣的朋友可阅读好书来成长,此系列主讲有理由爱Sqlserver的论证性文章,希望读者们看完后,可自行做出判断,Sqlserver是否真的合适自己,目的已达成。渴望自动化及使用场景笔者所最能接触到的群体为Excel、PowerBI用户群体,在Excel中,我们知道可以使用VBA、VSTO来给Excel带来自动化操作..._sqlsever 数据分析
随便推点
智慧校园智慧教育大数据平台(教育大脑)项目建设方案PPT_高校智慧大脑-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读294次,点赞6次,收藏4次。教育智脑)建立学校的全连接中台,对学校运营过程中的数据进行处理和标准化管理,挖掘数据的价值。能:一、原先孤立的系统聚合到一个统一的平台,实现单点登录,统一身份认证,方便管理;三、数据共享,盘活了教育大数据资源,通过对外提供数。的方式构建教育的通用服务能力平台,支撑教育核心服务能力的沉淀和共享。物联网将学校的各要素(人、机、料、法、环、测)全面互联,数据实时。智慧校园解决方案,赋能教学、管理和服务升级,智慧教育体系,该数据平台具有以下几大功。教育大数据平台底座:教育智脑。教育大数据平台,以中国联通。_高校智慧大脑
编程5大算法总结--概念加实例_算法概念实例-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读9.5k次,点赞2次,收藏27次。分治法,动态规划法,贪心算法这三者之间有类似之处,比如都需要将问题划分为一个个子问题,然后通过解决这些子问题来解决最终问题。但其实这三者之间的区别还是蛮大的。贪心是则可看成是链式结构回溯和分支界限为穷举式的搜索,其思想的差异是深度优先和广度优先一:分治算法一、基本概念在计算机科学中,分治法是一种很重要的算法。字面上的解释是“分而治之”,就是把一个复杂的问题分成两_算法概念实例
随笔—醒悟篇之考研调剂_考研调剂抑郁-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读5.6k次。考研篇emmmmm,这是我随笔篇章的第二更,原本计划是在中秋放假期间写好的,但是放假的时候被安排写一下单例模式,做了俩机试题目,还刷了下PAT的东西,emmmmm,最主要的还是因为我浪的很开心,没空出时间来写写东西。 距离我考研结束已经快两年了,距离今年的考研还有90天左右。 趁着这个机会回忆一下青春,这一篇会写的比较有趣,好玩,纯粹是为了记录一下当年考研中发生的有趣的事。 首先介绍..._考研调剂抑郁
SpringMVC_class org.springframework.web.filter.characterenco-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读438次。SpringMVC文章目录SpringMVC1、SpringMVC简介1.1 什么是MVC1.2 什么是SpringMVC1.3 SpringMVC的特点2、HelloWorld2.1 开发环境2.2 创建maven工程a>添加web模块b>打包方式:warc>引入依赖2.3 配置web.xml2.4 创建请求控制器2.5 创建SpringMVC的配置文件2.6 测试Helloworld2.7 总结3、@RequestMapping注解3.1 @RequestMapping注解的功能3._class org.springframework.web.filter.characterencodingfilter is not a jakart
gdb: Don‘t know how to run. Try “help target“._don't know how to run. try "help target".-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读4.9k次。gdb 远程调试的一个问题:Don't know how to run. Try "help target".它在抱怨不知道怎么跑,目标是什么. 你需要为它指定target remote 或target extended-remote例如:target extended-remote 192.168.1.136:1234指明target 是某IP的某端口完整示例如下:targ..._don't know how to run. try "help target".
c语言程序设计教程 郭浩志,C语言程序设计教程答案杨路明郭浩志-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读85次。习题 11、算法描述主要是用两种基本方法:第一是自然语言描述,第二是使用专用工具进行算法描述2、c 语言程序的结构如下:1、c 语言程序由函数组成,每个程序必须具有一个 main 函数作为程序的主控函数。2、“/*“与“*/“之间的内容构成 c 语言程序的注释部分。3、用预处理命令#include 可以包含有关文件的信息。4、大小写字母在 c 语言中是有区别的。5、除 main 函数和标准库函数以..._c语言语法0x1e